|
|
|
Schottky Diode Application Selection Guide
Mixer Diodes
|
|
Alternatives:
1. Integrated Circuit Mixers
2. Discrete transistors as active mixers
Features:
higher IP3 and less distortion than IC mixers
high barrier height + high drive produce low distortion
connecting diodes in series is a technique that can be used to increase barrier height
Key Parameters:
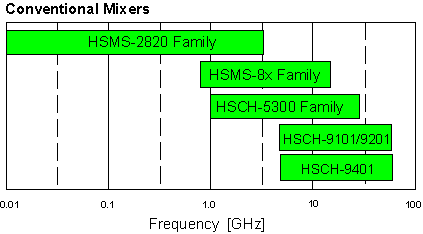
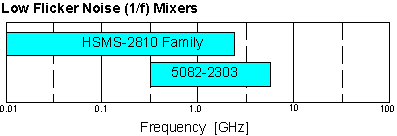
- Frequency range (f):
- SMT packages cover kHz to 12 GHz
- Noise Figure (NF):
- 6.5 - 7.5 dB (approximately equal to the insertion loss of the mixer)
- Rs and Cj combine to influence noise figure
- Rs must be low (5 - 7
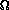 ) )
- Cj must be low (<1pF for use to 1 GHz, < 0.5 pF for use above 1 GHz)
- Cj is 0.25 pF for HSMS-820x: good as mixer to 12 GHz!
- Intercept point (IP3):
- based on LO drive level
Markets:
TV satellite receivers (DBS, TVRO)
Cellular, PCS Infrastructure and high linearity applications
ISM (Industrial-Scientific-Medical unlicensed band use)
Mixer Diode Terms
Frequency range (f):
- What:
- the frequency range over which a Schottky diode can make a useful mixer.
- Goodness:
- needs to match the requirements of the application.
Barrier height
- What:
- The term "Barrier height" is related to the voltage required for a given current in a Schottky barrier diode. Low voltage corresponds to low barrier height. Barrier height also sets Vf, the voltage at which the diode starts to clip.
- Goodness:
- depends on application - the Vf must match the desired clipping voltage.
Third Order Intercept Point (IP3)
- What:
- An indication of the amount of power that can be input into a mixer without causing distortion. Output intercept point quotes the output power level at which the third order intermodulation product curve intersects the Pout vs. Pin curve, in dBm. Input intercept point references this level to the input of the mixer by subtracting the mixer gain.
- Goodness:
- higher is better.
Noise figure (NF)
- What:
- Noise figure is a measure of the noise (low level distortion) added to the signal by a mixer.
- Goodness:
- lower is better.
|
|





