 products: products:
Function:
A vector modulator combines two orthogonal digital data streams with a high frequency carrier to encode the digital information in the phase characteristics (and sometimes in the amplitude characteristics) of the RF signal created by the modulator. Consequently, vector modulators are modulators that can produce output signals at varying magnitudes and at any phase angle. Since these modulators are commonly used to perform QPSK modulation, they are sometimes refered to as QPSK modulators.
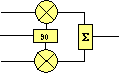
A typical topology consists of two mixers, a summer, and a phase shifter. One mixer handles the I data, the other handles the Q data. The purpose of the phase shifter is to ensure the the two mixers are operating othogonally (i.e. 90 degrees out of phase). Phase shifters may be implemented in a variety of ways; two common methods include cascaded flip-flops and RC networks. Most Agilent Technologies IC modulators use RC phase shifter circuitry. This circuitry tends to be the limiting element in the effective frequency range of the modulator. At the edges of the band the phase shifter introduces excessive phase errors by producuing a phase shift significantly different from 90 degrees.
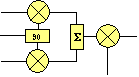
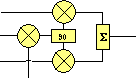
Modulators may incorporate additional mixers to improve performance. In a dual conversion modulator, the mixer follows the modulator. In an offset loop modulator, the mixer preceeds the modulator. In both cases the goal is to ensure that the output signal is at a different frequency than the incident RF carrier, so that feedback through the modulator cannot pull the frequency of the carrier and introduce modulation errors.
Schematic Symbols:
| direct conversion |
dual conversion |
offset loop |
 |
 |
 |
Agilent Technologies Products for Vector Modulatorr Applications
- Integrated Circuits:
- comparison of ICs
| 




